+++++++++++++
Advanced Calculator Enginering
+++++++++++++
—-—-
Conversion
The Conversions module will convert a given value into a new value using a
different unit of measurement.
Conversion Procedure:
- Select a conversion type from the “Select One†drop-down box
-Select a beginning unit from the “Select Entered Unit†drop-down box.
This will be the unit for the data you want to convert.
-Select an ending unit from the “Select Unit to Convert to†drop-down box.
This will be the unit the data will be converted to.
- Enter your data in the textbox that appears after all three drop-box options are filled.
- Press the Enter key to display conversion.
- You may now enter more data to convert or you may select new units or
conversion type.
—-—-—-
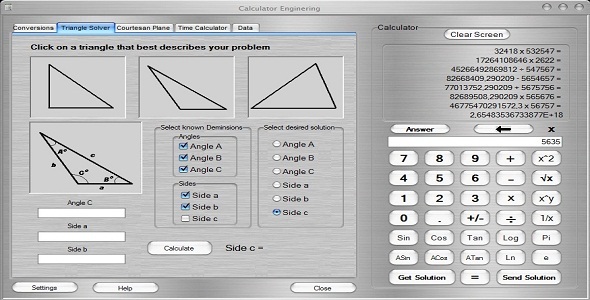
Triangle Solver
The Triangle Solver module computes a solution for unkown angles or sides of
a triangle based on data provided for the known dimensions of the triangle.
Triangle Solver Procedure:
- Select a triangle from the top of the page that best describes shape of the triangle
you are trying to solve. These triangles are for reference only and an exact
match is not necessary.
- Once a general triangle shape has been selected, a reference triangle will appear to
to assist solving your triangle. Use the diagram to select which sides and
angles you have dimensions for and which sides or angles you need to solve.
As with the triangles that were originally selected, this triangle is for reference
only and an exact match with your triangle is not necessary.
- Using the reference triangle, select the checkboxes that correspond with the known
dimensions of your triangle. Data will be entered in later. The checkboxes are
only used to determine which deminsions to prompt for or to determine if there
is enough data to solve the triangle.
- Select which dimension you need solved using the buttons under “Select desired
solutionâ€. Only one solution can be selected at a time.
- Once you have selected a desired solution and have selected all known dimensions,
textboxes will appear on the lower left portion of the page along with labels
describing what data must go in each textbox.
Note – If no textboxes appear when you have selected a desired solution,
then there is an insufficient number of known deminsions. Try to
aquire more data on your triangle in order to solve for your solution.
- Fill in the textboxes with appropriate data prompted by labels above the textboxes.
All prompted data must be filled in order to compute a solution.
Note – Angles are entered in Degrees.
- Once all data textboxes are filled click the “Calculate†button to compute the solution.
- The solution will be displayed to the right of the Calculate button. You may now select
a different triangle, solve for a different dimension, or simply change data in
the textboxes for a different solution.
—-—-—-
Courtesan Plane
The Courtesan Plane module is intended to give position and dimension data based
on two points of a courtesan plane enterd in ( X , Y ) format. The module
will compute the linear distance between the two points, the midpoint,
slope magnitude, and angles. Slopes and Angles are given in both
directions – relative to the X-axis and relative to the Y-axis. Slopes are
computed such that the line between the two points can be defined as
a functions [ y = (Slope From X-Axis)x ] and [x = (Slope From Y-Axis)y].
If two points are not known, then a solution can be computed using
distance, midpoint, slope, or angle in conjunction with a beginning
point or the midpoint. A list of entry options are availiable in a drop-box
at the top of the Courtesan Plane page.
Courtesan Plane Procedures:
- Select a data entry option from the drop box at the top of the page.
- Enter in the data prompted by the textboxes. Angles are entered in Degrees.
Distance can be positive of negetive. Slope must be in decimal format.
- After all position data is entered, click the “Calculate†button to display the
solutions at the bottom of the page.
- A solution of “NaN†or “Infinity†indicates there is no solution for that field.
Example:
Point #1 = ( 30.5 , 42 )
Point #2 = ( 30.5 , 58 )
Slope From X-Axis = -Infinity ; There is an infinite slope.
Angle From Y-Axis = NaN ; The line between the two points
is parallel with the Y-Axis.
—-—-—-
Time Calculator
The Time Calculator module has two functions. The left column allows you to enter a
beginning time and an ending time, then the elapsed time is solved. A drop-box
lets you select what format the solution will be displayed. The right column
allows you to enter a beginning time and an elapsed time, then the ending time
is solved.
Beginning – to – Ending Time Procedures:
- Using the checkbox at the top of the page, select whether your time data will be in
standard time or in military time.
- Enter your beginning time data, using hh:mm:ss format. This can be done two ways;
using the up / down arrows in each data field to increment / decrement the
value or you can select the data field and type in the value.
Value limits are as follows:
Days – 100
Hours – 12 (24 if selected Military Time)
Minutes – 60
Seconds – 60
AM / PM selection on valid in Standard Time
- Enter your ending time given the same format as above.
- Click the “Calculate†button to compute the solution
- The output format chosen by the “Solution Format†drop-box can be selected
before or after the solution is computed. If “Hours†or “Minutes†are chosen
the output will be in decimal form. Decimal accuracy can be set in the Settings
page under the “Time†setting.
Beginning – Plus – Elapsed Time Procedures:
- Select Standard or Military time and enter in beginning time data as previously
described in “Beginning – to – Ending Time Proceduresâ€
- Enter in the value of elapsed time to be added to your beginning time. As with
the beginning time, data can be entered using either the up / down
arrows or keyboard entry. The value may be any unit (Day, hour, minute,
second) or a combination of units, i.e. 1 Day, 2 Hours, and 15 minutes
could be one whole entry. Value limits are as follows:
Days – 100
Hours – 9999
Minutes – 9999
Seconds – 99999
- Click the “Calculate†button to compute the solution.
- The solution will be displayed in time format – Days and then hh:mm:ss. If
Military Time is not selected, the solution will also contain AM or PM.
—
Data
The Data module will convert data types such as Hexidecimal, Binary, Decimal,
Binary Code Decimal, and ASCII.
Data Procedures:
- First select which data type will be entered to be converted. Only one may be
selected at a time.
- Enter in the data to be converted in the textbox to the right of the Input selection.
Hex data input is limited to one word ( 4 characters ). Decimal data
input is limited to whole numbers and a value of 65,535 or less. Binary
data input is limited to one word ( 16 bits ). BCD data input is limited
to 4 digits. ASCII data input is limited to one character.
- Press the Enter key to display the conversion solution at the bottom portion of
the page.
- You are then able to enter different data to convert or change the input data type.
Advanced Calculator Enginering (Windows)
No comments:
Post a Comment